Background and Identification
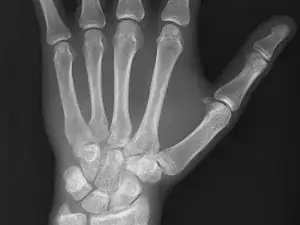
X-ray machines are used in medical imaging and radiography to view images of anatomical structures in the body. They function by emitting short bursts of high-energy electromagnetic radiation in the 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz range. These waves are passed through the body and picked up by a detector on the other side, with some of the waves being absorbed by different parts of the subject based on structure and density. This allows X-ray techs to view skeletal, muscular, or even venous systems without invasive means.